Uterine Fibroids: Benign Tumors in Uterus
Uterine fibroids are growth in the wall of the uterus, which is almost non-cancerous i.e., benign. Uterine fibroid is also known as uterine myoma, uterine leiomyomas. Most of the uterine fibroids occur in the body and fundus of the uterus and only three percent of fibroids occur in the cervix i.e., neck of the uterus. Mostly uterine fibroids shrink as estrogen and progesterone hormone decline after menopause. Uterine fibroids can be co-related with Grabashya Gata Granthi, which is mentioned in the Ayurvedic texts about tumor in uterus treatment.
Facts about Uterine Fibroids
- Uterine fibroids are benign i.e., non-cancerous growth and do not indicate any kind of carcinoma of the uterus. These are more common than the malignant tumors.
- Fibroids are more common in the childbearing age of women.
- Uterine fibroids have become the most common cause for uterus removal i.e., hysterectomy.
- The most widely experienced first symptom of uterine fibroids is difficulty in conception.
- Women with uterine fibroids can conceive. The most common issue is the early separation of placenta i.e., placental abruption.
- Women with high BMI i.e., obese women are at high risk of uterine fibroids.
- Anti-hormone medication may help in the shrinkage of fibroids.
- Approximately 80% of women suffer from uterine fibroids.
- Women who drink alcohol are at elevated risk of uterine fibroids.
- Surgery is not the only option to treat uterine fibroids.
- African women are at a higher risk of uterine fibroids than Asian women.
- Women who only give birth once are at a lower risk of having uterine fibroids.
- In the United States, approximately three lakh hysterectomies (removal of uterus) are done due to uterine fibroids.
- Embolization is the safest treatment that is used for uterine fibroids. Its success rate is approximately 94%. Reoccurrence after embolization is very rare.
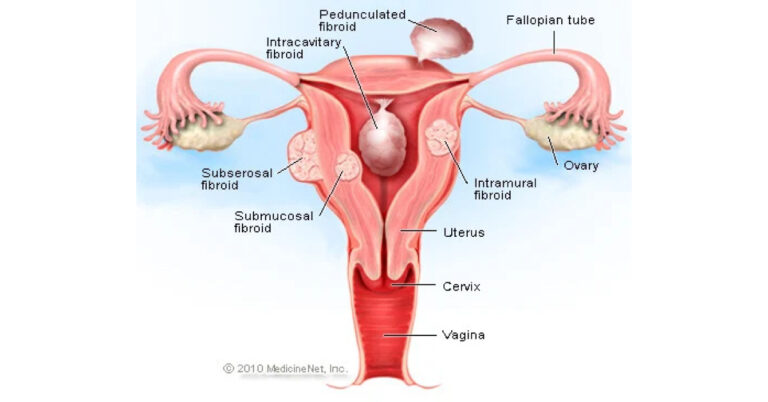
Uterine Fibroids Types
Modern point of view
- Sub-serosal Fibroids- This type of fibroids is very large and are situated under the peritoneal (mucosal) surface of the uterus. These may become pedunculated fibroids that detach from the surface and become parasitic leiomyoma.
- Sub-mucosal Fibroids- This type of fibroids distort the uterine cavity and are located beneath the endometrium layer of the uterus. Even a small lesion in the location may lead to infertility and bleeding. The pedunculated type can pass through the cervix and is known as the intracavity fibroid.
- Intramural Fibroids: Intra-mural type of fibroids is the most common type of fibroids of the uterus and are usually asymptomatic. This type of fibroids is located on the wall of the uterus.
- Cervical Fibroids: This type of uterus fibroids is mainly located on the wall of the cervix area i.e., in the neck of the uterus. They are rarely located in the broad ligament, round ligament, uterosacral ligament, smooth muscle tissues.
Ayurvedic point of view
There are 5 types of Garbhasya Gata Granthi
- Vaataja- This type of Granthi (fibroids) is painful and elongated. Vattaja Granthi of Grabhashya is co-related with subserosal fibroids which are even and very large.
- Pittaja- This type of Granthi is prone to inflammation and suppuration. Pittaja Grabhashya granthi can be considered as submucosal fibroid.
- Kaphaja- Kaphaja Grabhashya Granthi can be co-related with cervical and intramural fibroids. These fibroids have mild pain and are localized.
- Medo Granthi- Medo Granthi usually have mild pain and are broad. These can be characterized by degenerative changes in fibroids.
- Sira Granthi – Sira Grabhashya Granthi is also characterized by degeneration in fibroids. This type of fibroid has a quick onset and usually has multiple symptoms and complications.
Some authors also consider two other types of Granthi i.e., Rakataja and Mansaj Granthi.
Uterine Fibroids Causes
Ayurvedic point of view
As per Ayurveda, the aggravating factors of Grabhashya Granthi vary from type to type. The main causes are as follows:
- Vattik Grabhashya Granthi: Excessive intake of Tikat (bitter), Kashaya (astringent), Katu (pungent) Aahar (food). Ruksha (dry) food and nerve-wracking conditions like Chinta (excessive thinking), Bhaya (fear), Shoka (grief), etc may also lead o Vattaja Granthi.
- Pittaja Grabhashya Granthi: Excessive intake of Aahara (food) i.e Amala (sour), Lavana (salty) lead to Pittaja Grabhashya Granthi. Krodh (excessive anger), Tailiya Pradarth (fried food) are also major causes.
- Kaphaja Grabhashya Granthi: Leading Sukumara Jeevan (desk-bound lifestyle) and excessive intake of Atti Madhur(sweet), Snigadh (oil) Aahar food are major causes.
- Madya Pana (alcohol intake)
- Atti-Bhojan (overeating)
- Diva Swapana (sleeping during daytime)
- Ratri Jagarana (staying awake at night)
Modern point of view
- Hereditary: Family history of uterine fibroids
- Hormones: Imbalance in hormones i.e., estrogen and progesterone may also lead to uterine fibroids.
- Excessive intake of alcohol
- Obesity
- Increase the quantity of ECM i.e., extracellular Matrix that helps in sticking cell
- Contraceptive use
- Eating a large quantity of red meat and less intake of fruits and vegetables
- Vitamin D deficiency in the body
Uterine Fibroids Symptoms
Ayurvedic point of view
- Toda (pricking pain)
- Mathya or Vruschati (churning pain)
- Aayamate (pulling pain)
- Raktatti Pravritti (menorrhagia) seen in sub-mucous fibroids
- Aadhmana (heaviness in the abdomen) seen in sub-serous fibroids
- Aartava Rooja, Presta Vamshana Rooja (congestive dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain, backache)
- Bahu Mutrata (excessive urination)
- Yoni Strava (vaginal discharge)
- Chira, Achira Abhivrridhum (may develop slow or fast)
- Vivandh (constipation)
- Katti Shool (backache)
Modern point of view
- Constipation
- Vaginal discharge
- Low backache
- Dyspareunia (pain during sexual activity)
- Pressure on the bladder due to fibroids lead to frequent urination
- Bloating i.e., fullness in the bladder
- Not being able to evacuate the urine properly
- Excessive bleeding during menstruation
- Painful bleeding (dysmenorrhea)
- Pain during passing stool
- Spotting before and after periods
- Pain in legs
Ayurvedic Treatment of Uterine Fibroids
- Management according to Samprapti Vighatana (to break the pathogenesis)
- Vaataanuloman (balancing Vata)
- Lekhan (scrapping therapy)
- Chedan (excision method)
- Visravana (use of needles for draining of pus or purpose of bloodletting)
- Raktprasadan (blood nourishment therapy)
- Kapha-Vatahar drugs
- Rasayana therapy (rejuvenation therapy)
Herbs
- Kanchanara (Bauhinia variegata)
- Punarnava (Boerhavia diffusa)
- Guggul (Commiphora mukul)
- Haridra (Curcuma longa)
- Mulethi (Glycyrrhiza glabra)
- Shatavari (Asparagus racemosa)
- Ashoka (Saraca asoca)
- Isabgol (Plantago ovata)
- Madhuka (Madhuca longifolia)
- Jambu (Syzygium cumini)
- Aagru (Aquillaria agallocha)
- Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
- Bharangi (Clerodendron serratum)
At Yukti Herbs, all these herbs are available in best quality available in a packing of 60 capsules, which means 1 full month of supply!!
Dos and Don’ts
- Keep a check on blood pressure. Fibroids have a strong link with hypertension.
- Limit intake of salt as it can increase the risk of formation of fibroids.
- Include organic cruciferous vegetables and fruits and whole grains in your daily diet.
- Avoid caffeine, processed food, and alcohol.
- Avoid smoking. Smoking decreases the oxygen supply to the pelvic region resulting in various symptoms.
- Maintain healthy BMI level. In obese people, there is more secretion of estrogen which results in fibroids.
- Avoid contact with chemicals found in dyes, paints, non-stick coating, plastic with BPA, etc.
- Elevate your legs with pillow to avoid pain during menstruation.
When to see a doctor
If you are suffering from the symptoms given below, the you must consult a doctor:
- Continuous pelvic pain
- Heavy periods
- Painful periods
- Difficulty in urination
- Spotting in between the menstrual period
- Low RBC count
Conclusion
Uterine fibroid is a disease of the female reproductive system. This benign tumor results in various associated symptoms like dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, etc. In modern gynecological practice, no definite treatment for uterine fibroid is available. According to Ayurveda, uterine fibroids can be co-related with Garbhasya Gata Granthi, which occurs due to vitiation of Vata, Kapha with Rakta, and Mansa. In Ayurveda, various herbs and formulations along with Sashtra Chikitsa (various surgical procedures) help to treat Garbhashya Gata Granthi from roots.
At Yukti Herbs, all the recommended herbs are available in best quality available in a packing of 60 capsules, which means 1 full month of supply!!!
Book your free ayurvedic specialist doctor consultation online @ www.yuktiherbs.com or email at yuktiherbs@gmail.com. You may also call or WhatsApp at +91 828-386-5637 and +91 752-786-9388.